Hello readers👋
Advancements and innovations in the crypto space every day. As you would have heard of Decentralized finance or Defi, well it's an exciting space. But if you don't know what Defi is, this blog is for you!
Let’s dig a little deeper into DeFi and learn more about it.
Introduction
What is Defi?
Defi stands for 'Decentralized finance'. It refers to financial applications built on blockchain technology that enable digital transactions between multiple parties.
Before understanding what Defi actually is, let us first understand centralized or traditional finance.
Consider the following example scenario.
Suppose a person named Luv has some money and he wants to earn interest on that money. What will he do?
You are right!
He will deposit it in any bank and earn interest on that.
Suppose another person named Khush wants to open a new business and for which he requires some money. What will he do?
You are right again!
He will take a loan from a bank by giving something as collateral to the bank and he will be charged interest on the loan
What do banks do in this scenario here?
Banks deposit money of Luv's and gives him less interest and give a loan to Khush by charging high interest on it.
i.e Banks act as a centralized trusted party here.

This is an example of traditional finance. Let us understand it more formally.
Traditional finance
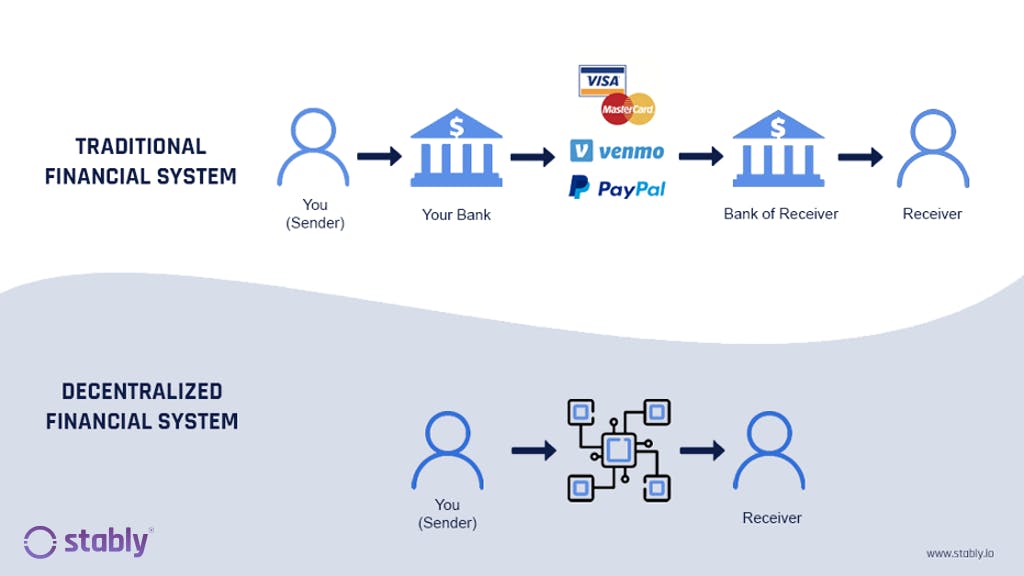
It refers to a central authority say banks covering the flow of money. The financial system is full of third parties that facilitate money movement between parties, with each one charging fees for using their services.
In traditional finance, banks and government have complete control over your money and control over the financial system.
For example - banks can stop you from creating a bank account, the government can print more currency notes if they like, etc.
Well all of us currently deposit money in banks and have trust in them. But are they really trustworthy? What are some of the cons of this system?
Let us have a look!
Cons of traditional finance
🔸Expensive
🔸KYC required
🔸Country limited
🔸Prone to censorship
🔸Not transparent
🔸Slow transaction times
🔸Banks have complete control over them
Traditional finance is expensive
Banks charge some amount of money to be paid by a customer for using their services which is quite high. Ex - banks charge high interest on loans, charges for debit and credit cards, etc. Hence, it is quite expensive.
Traditional finance requires KYC
It relies upon KYC(Know your customer) which refers to procedures that financial organizations use to verify a client’s identity and legitimacy before doing business with them. In short, a customer must prove they are who they say they are.
Traditional finance is country limited and prone to censorship
The traditional financial sector comes with a lot of rules, regulations, and requirements that make it difficult for people across borders to transact business. Therefore, it is prone to censorship.
Traditional finance is not transparent
Once you deposit your money in the bank, you can't track where your money is being lent to or where it is used. You only deposit with the trust you have in the system.
Banks have complete control over them
For example - Banks are free to implement negative interest rates, meaning customers start paying the bank to hold their funds.
Before moving further, I would like to make you understand what fiat money refers to?
Fiat money is a government-issued currency that is not backed by a commodity such as gold. Fiat money gives central banks greater control over the economy because they can control how much money is printed. Example - US Dollar, Euro, etc.
Now let us look at banks for cryptocurrencies i.e Centralized finances.
Centralized finance (Cefi)
Cefi - The bank for cryptocurrencies.
What do you think about how are cryptocurrencies traded between people? How can I send 1 ether to my friend or how can I convert my ether to bitcoin?
Before Defi was introduced, Centralized Finance was the standard for trading cryptos. In centralized finance (CeFi), all crypto trade orders are handled through a central exchange generally known as CEXs.
Cefi is a type of financial practice within the cryptocurrency sphere where users can earn interest and get loans on their digital assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, USD Coins like USDT & USDC, and so on, through a centralized platform.
Centralized crypto exchanges (CEXs) are owned by a business or a company.
For example, both PayPal and Coinbase could constitute as CeFi as they both offer fiat-gateways to payments services alongside crypto custodial services. Binance is another example of Cefi.
Generally, when a person enters the crypto space for the first time they tend to do it through a centralized exchange (CEX). CEXs provide the exchange between cryptocurrencies and native currency that makes buying, trading, and holding crypto simple.
You don’t own your cryptocurrencies when buying /selling via a centralized exchange. Moreover, you are subject to the rules a centralized exchange imposes on you. Also, you are subject to the rules set by the centralized exchange.

Pros of Cefi
🔸Fiat gateway
🔸Simple to use
🔸No risk of losing private keys
🔸Exposure to a wide range of crypto assets
Cons of Cefi
🔸If a CEO or keyholder goes missing, funds could be locked and withdrawals suspended without notice
🔸Users do not physically own their crypto assets.
What do you observe?
As you have seen, centralized finance or traditional finance completely works on how much we trust them.
Can we have some sort of finance in which it is not necessary to have trust in any of these third parties?
To have them 'Decentralized'.
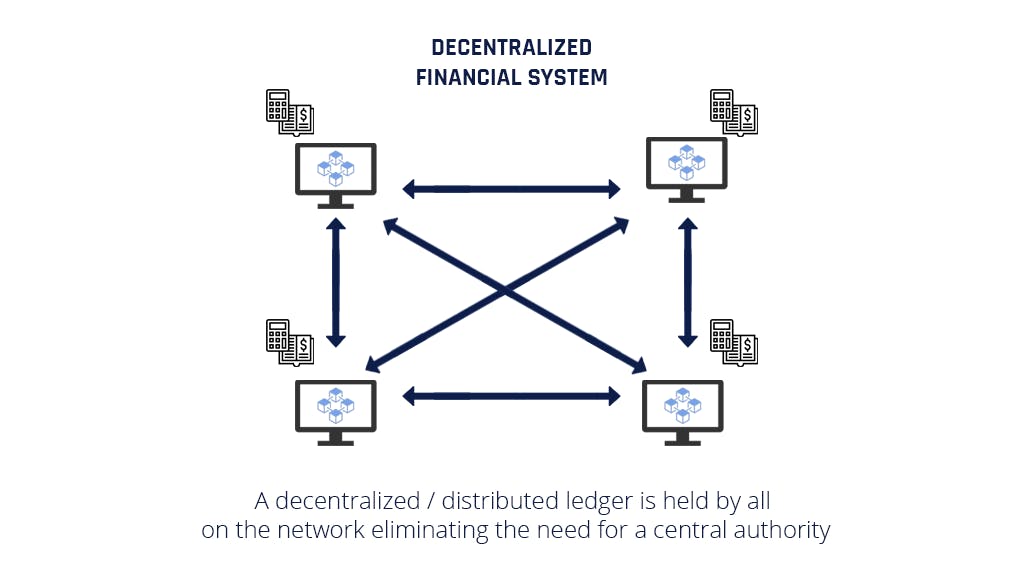
Decentralized finance
Decentralized finance is a financial service that utilizes a set of smart contracts and algorithms to execute its services. The contracts are automated agreements that don’t require intermediaries or banks.
These contracts run on the Ethereum network and use blockchain technology.
Defi happens without a central authority, or the involvement of banks or other traditional financial organizations, hence “decentralized.”
DeFi can involve lending crypto, sending crypto, or investing crypto.
From anywhere you have an internet connection, you can lend, trade, and borrow using software that records and verifies financial actions in distributed financial databases.
A distributed database is accessible across various locations; it collects and aggregates data from all users and uses a consensus mechanism to verify it.
In defi, users deposit their funds to be managed by smart contracts. No company or individual has access to the funds.
TradFi vs Defi
Let us now understand the difference between traditional finance and decentralized finance.
The primary purpose of Defi is to provide access to basic banking products like savings accounts or loans to anyone in the world without fear of censorship or restriction, and with full transparency because of the blockchain ledger.
Cefi vs Defi
The question here is users should trust technology or people.
With DeFi, users trust that the technology will perform as proposed to execute on services being offered. With CeFi, users trust a business’s people to manage funds and execute the business’s services.
Though funds are stored on the exchange, they are kept outside of users’ custody and are vulnerable to threats in case the security measures put in place by the exchange fail.
Due to this, centralized exchanges have been the target of various security attacks.
Since defi has some cons but still Defi has the potential to disrupt traditional or centralized finance because of its ability to be a financial tool that is outside of any control by the government or any company.
Pros of Defi
🔸No KYC required
🔸Not country limited
🔸Completely transparent
🔸Permissionless
🔸Trustless
🔸Censorship resistant
🔸Cheaper
Defi is trustless
You don’t need to worry about whether the platform will run as intended or not because you can verify the DeFi services by auditing the codes. Besides, you can also use external tools such as Etherscan to check if a transaction was executed correctly.
Defi is permissionless
Users do not require permission to use DeFi. Users can directly access the services using a wallet and without providing personal information or depositing money with DeFi. It is openly accessible to all parties, without any barrier or discrimination.
Well talking about pros of defi, let us also look at some cons of defi.
Cons of Defi
🔸Complicated
🔸Responsibility for own private keys
🔸No customer service
🔸Relatively high Ethereum gas fees
Pillars of Decentraziled finance
- Stablecoins
- Lending and borrowing
- Decentralized exchanges
- Insurance
Stablecoins
Let us understand what stablecoins are.
Before understanding it, we first understand what does pegged currency mean? Pegged digital currencies are those that are linked to the specific value of a bank-issued currency or other commodity. Pegging a currency stabilizes the exchange rate between countries.
What are stablecoins?
A stablecoin is a digital currency that is pegged to a “stable” reserve asset like the U.S. dollar or gold. Stablecoins are designed to reduce volatility relative to unpegged cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Stablecoins bridge the worlds of cryptocurrency and everyday fiat currency because their prices are pegged to a reserve asset like the U.S. dollar or gold.
Example of stablecoins -
🔸Tether (USDT)
🔸USD coin (USDC)
🔸Binance USD (BUSD)
🔸Dai
🔸TeraaUSD (UST)

Stablecoins dramatically reduces volatility compared to something like Bitcoin and results in a form of digital money that is better suited to everything from day-to-day commerce to making transfers between exchanges.
Stablecoin is referred to as a utility token because it allows you to quickly buy and sell on decentralized exchanges that do not accept fiat currencies.
Stablecoins are also used in centralized exchanges. What makes them useful in an exchange of this kind is the fact that fiat currencies take a long time to process, but their tokenized counterparts are standard blockchain entities that move quickly.
Stablecoins can be used as an everyday currency
Unlike traditional crypto coins, which are subject to price fluctuations and volatility, stablecoins do not fluctuate much because they are backed by national currencies.
In addition, they have the same advantages as other crypto coins: blockchain security, transaction anonymity, quick transfers, and the lack of intermediaries. They can be used to pay for groceries, fares, or electricity bills, among other things.
Stablecoins have great potential for smart contracts
Frequent price changes in cryptocurrencies can have an unpredictable impact on the contract’s terms. The use of stablecoins can provide contract stability and ensure that more secure contracts are enforced by the blockchain.
Example -
Suppose you bought 1 Ethereum at 1500$ and now the current price of Ethereum is (say) 2500$. Now you want to sell your ether to earn profits.
Without stablecoins, you have to sell your ether at a centralized exchange like coinbase or binance and in return, they give USD to you. Also, they would take some part of your transaction as fees of the service provided.
Next, you have to wait for coinbase or binance to give it to your bank, and then you are able to withdraw it from the bank.
Suppose now Ethereum drop to 500$ and you want to buy more ether so you deposit your money (say 2500$) from the bank back into coinbase or binance and then you wait for your transaction to clear and buy 5 ether(5*500=2500) and hold them.
In this system, there is a lot of taxes, fees, and waiting and hence this process is too cumbersome.
The use of stablecoins can solve this issue.
With the use of stablecoins -
For the previous example, you bought 1 ether ar 1000$ and it raises to 2500$. Here, you trade your 1 ether for 2500 USDC (stablecoin) and you just hold it. When ether drops to 500$, you trade your 2500 USDC for 5 ether.
It's that simple.
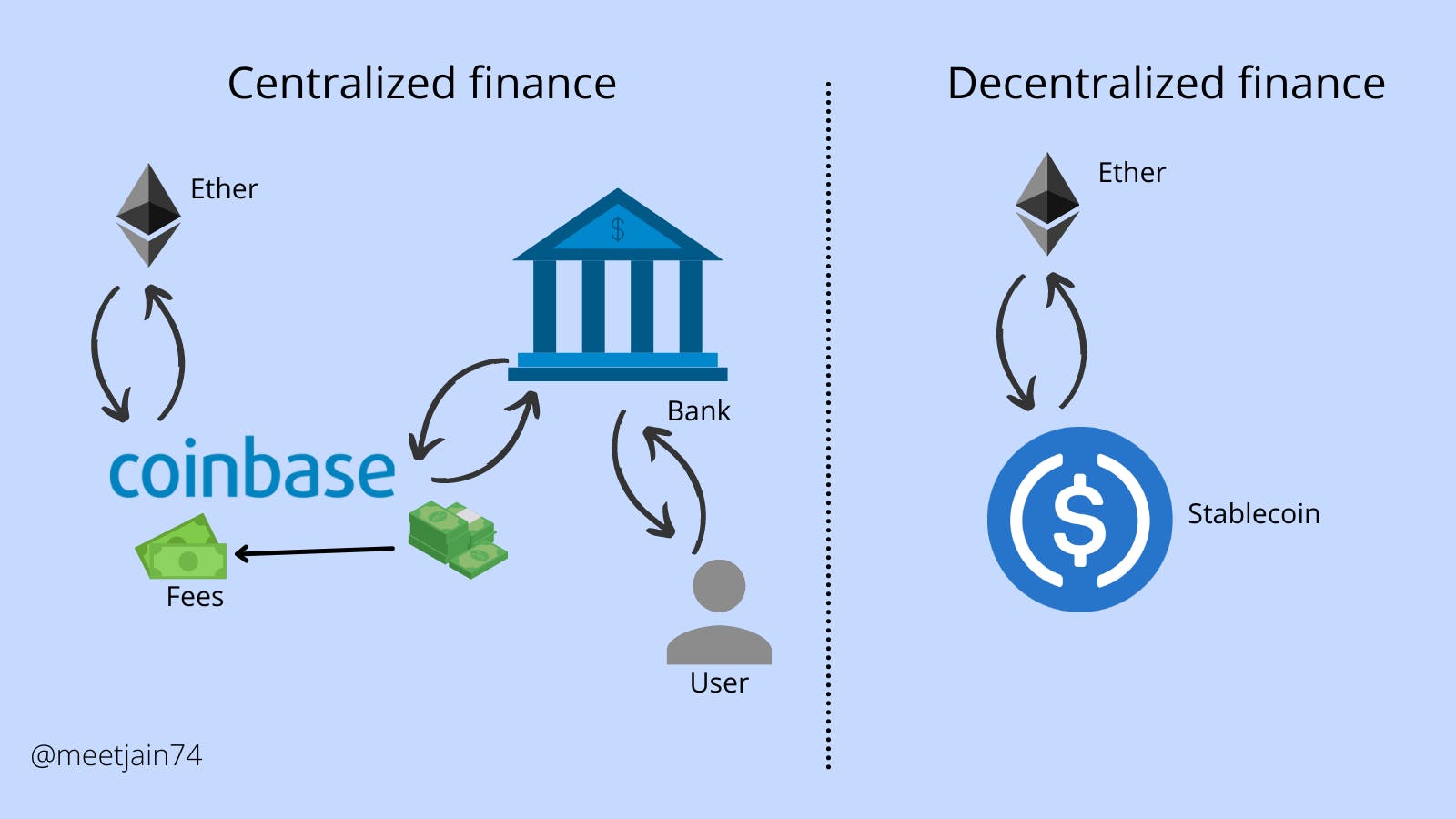
The fees in the case of stablecoins is also very less as a decentralized exchange is used for trade and it is also very fast i.e you do not have to wait for a long time. Also, the stablecoins are secure and you trust them because it is code that doesn't change.
Lending and borrowing
Moving back to the Luv and Khush example we discussed at the start, Luv wants to get interest on his crypto assets(here) and Khush wants to take a loan.
How does this happen in decentralized finance?
Let us understand
This happens through a Defi platform. On the DeFi platform, Khush can take a loan, allowing Luv to earn interest once the loan is returned. The lending process is executed from the start till the finish without intermediaries.
A coin holder sends the tokens they intend to lend into a pool using a smart contract. Once the coins are sent to a smart contract, they become available to other users to borrow.
Afterward, the smart contract issues tokens (usually, the platform’s native token ex - aTokens for Aave, cTokens for Compound, Dai for MakerDao) that are distributed out automatically to the lender.
In this system, a lender lends money to a borrower to expect the borrower to repay the loan in full. The borrower compensates the lender for temporarily releasing its funds.
Virtually all the loans issued via the native tokens are collateralized. This means that users who wish to borrow funds will need to provide a guarantee.
However, unlike the centralized financial system, the guarantee in the DeFi space is in the form of cryptocurrencies that are worth more than the actual loan itself.
i.e
These types of loans are over collateralized.
Well, you might be thinking you have to pay more for collateral than the actual loan which defeats the complete purpose of the loan.
However, there are numerous reasons why DeFi borrowing makes sense.
Ex -
A user wants to take a loan of 2000$ and he has 1 ether worth 2500$, he can put 1 ether as collateral and get a loan. The user doesn't want to sell the ether and get money because he believes that the ether value can increase in the future.
i.e
The users might require funds to take care of unforeseen expenses they may have incurred and don’t intend to sell their holdings as they believe the assets are due to an increase in value in the future.
Furthermore, by borrowing money via DeFi protocols, users can avoid or delay paying capital gains taxes on their cryptocurrencies.
Defi borrowing makes sense now.
Popular lending and borrowing protocols
🔸Maker (Dai tokens)
🔸Aave (aTokens)
🔸Compound (cTokens)
Now how do you exchange your coins or tokens of one cryptocurrency into another in a decentralized system?
What we have here is called - Decentralized exchange
Decentralized exchange
Decentralized exchanges or DEXs enable users to buy and sell cryptocurrencies with one another without the need for brokers. Users connect their crypto wallet to a DEX, select their crypto trading pair of choice, enter the amount, and hit the swap button.
The fees charged by DEXs are too low as compared to CEXs and DEXs are also not regulated by anyone, unlike CEXs where they have to abide by the government.
We can say that -
The code is the law in Defi which doesn't change
Popular DEXs
🔸Uniswap (major decentralized exchange on the Ethereum network)
🔸Pancake swap (on Binance chain)
🔸Curve
🔸Sushiswap
Defi Insurance
DeFi insurance refers to insuring yourself, or ‘buying coverage’, against losses caused by events in the DeFi industry.
Suppose you’re an individual or a company with capital locked somewhere on a DeFi platform. As you’re aware of the fact that you might lose your capital if this platform or protocol gets hacked, you want to insure yourself against this risk.
You, therefore, go to a DeFi insurance provider and pay a certain amount in order to get covered in case you lose your capital due to a specific, predetermined event.
The premium you pay for a cover widely varies depending on the cover type, duration, and provider.
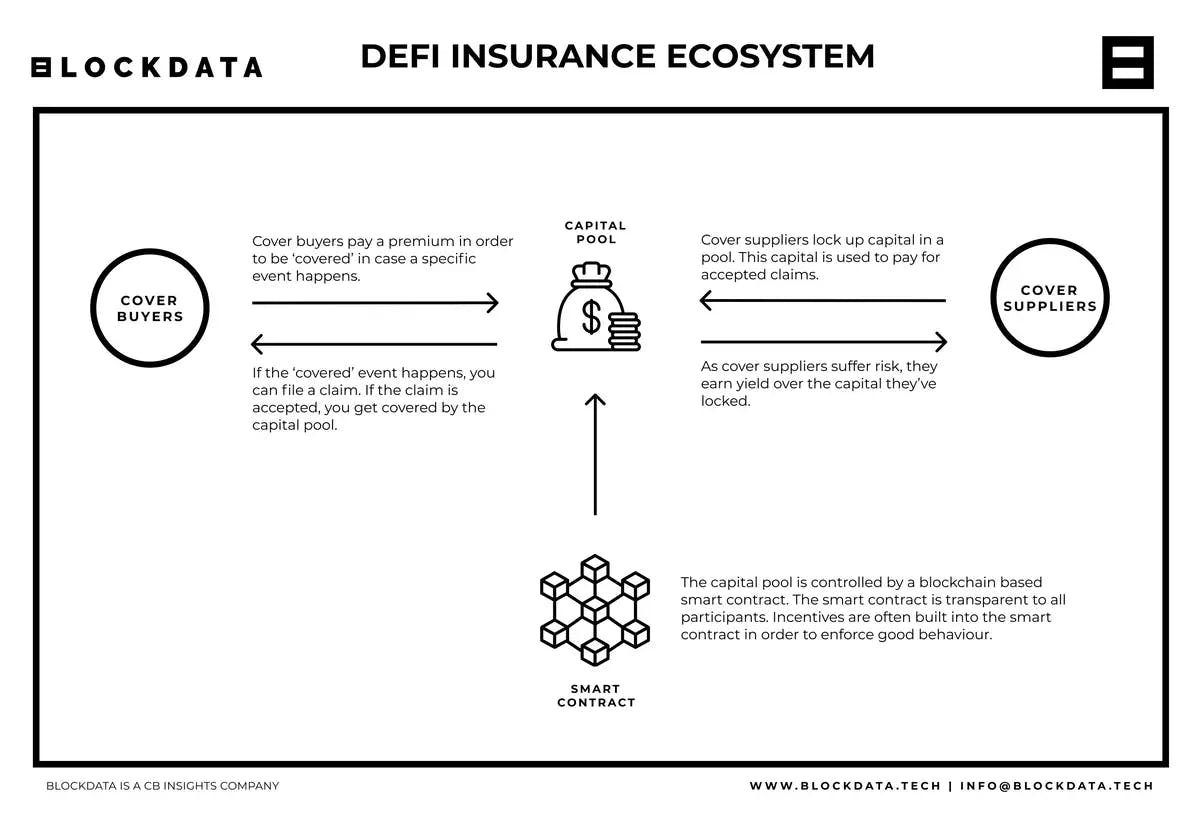
How does Defi Insurance work?
Instead of buying coverage from a single person or company, you buy coverage from a decentralized pool of coverage providers.
Anybody can act as a coverage provider. You do so by locking up capital in a so-called capital pool. By doing so, you effectively become a liquidity provider.
As a coverage provider, you choose for which events or protocols you want to provide coverage. You might, for example, be very certain that exchange X will not be hacked. You are therefore fine with providing liquidity to the capital pool which covers that specific event.
Should exchange X still be hacked, the funds in that capital pool will then be used to cover the claims from people who bought coverage against a hack.
As a coverage provider, you are of course exposed to risk. That is why you earn interest on the capital you lock up as a coverage provider. This interest is often (partly) paid for using the coverage buyers’ premium.
How are claims verified?
DeFi insurance protocols are frequently set up using a DAO structure. In such a structure, holding the token associated with the insurance protocol gives you governance rights. Meaning you can participate in voting to accept or deny claims.
Sometimes claims are automatically verified, instead of by community voting. This is often done with the help of so-called ‘oracles’. Oracles are decentralized information mechanisms that verify external data.
Oracles can be set up to accurately track the outcome of certain events, and distribute this information across the internet.
Now as we might have now understood what Defi is, let us look at some of its use cases.
Defi use cases
- Banking services
- Addressing global financial issues
- Circumventing Censorship and Restrictions
Banking services
Decentralized finance has the ability to provide financial services without geographical barriers. Traditional finance has struggled to reach some remote parts of the world, leaving billions without access to banking services.
Addressing global financial issues
Concerned by the threat posed by the current global financial systems, many people are looking to emerging technologies to shield themselves.
Circumventing Censorship and Restrictions
The traditional financial sector comes with a lot of regulations and requirements that, at times, make it difficult for people across borders to transact business.
What are the present challenges of Defi?
Challenges of Defi
One of the biggest challenges that could stop decentralized finance from replacing traditional finance systems is the aspect of people being forced to trust unregulated open-source code.
The fact that anyone can access a source code powering a decentralized finance system means anyone can hack smart contracts and steal all the keys, which could result in people losing substantial amounts of money.
The technology behind the decentralized finance application is still underdeveloped and unfriendly, and it will always be prone to vulnerabilities that would damage the technology’s reputation.
Summary
While the use of digital ledger technologies in the global financial system is still in the early days, one cannot dispute this technology’s ultimate potential.
Decentralized finance has what it takes to revolutionize the financial sector in a time of growing concerns about data and privacy security.
The fact that DeFi could result in so many people gaining access to banking services in areas where traditional finance has failed underscores its massive potential.
Decentralized finance will first have to address a number of issues pertaining to scalability, security, liquidity, and regulations if it is to replace today’s financial system.
Conclusion
This is the end of the blog.
I hope you might have understood what Defi is. Let me know your thoughts in the comment below.
Do like this blog and follow me!
Also, you could follow me on Twitter
Thanks for reading💛